By Gerald L. Maatman, Jr. and Jennifer A. Riley
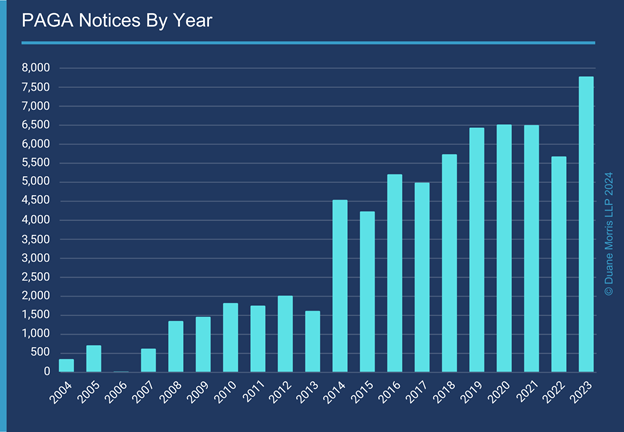
Duane Morris Takeaway: In 2023, employers saw claims filed under the California Private Attorneys General Act (PAGA) reach an all-time high. According to data maintained by the California Department of Industrial Relations, the number of PAGA notices filed with the LWDA has increased exponentially over the past two decades, from 11 in 2006 to 7,780 in 2023. The PAGA created a scheme to “deputize” private citizens to sue their employers for penalties associated with violations of the California Labor Code on behalf of other “aggrieved employees,” as well as the State. A PAGA plaintiff may pursue claims on a representative basis, i.e., on behalf of other allegedly aggrieved employees, but need not satisfy the class action requirements of Rule 23. In other words, the PAGA provides the plaintiffs’ class action bar a mechanism to harness the risk and leverage of a representative proceeding without the threat of removal to federal court under the CAFA and without the burden of meeting the requirements for class certification. If successful in prosecuting such a case, aggrieved employees receive 25% of any civil penalties and pass the other 75% to the California Labor and Workforce Development Agency (LWDA). The plaintiffs’ attorneys who pursue the action may collect their attorneys’ fees and costs.
Watch our Trend #6 video below, where Duane Morris partner Jennifer Riley discusses the PAGA filings explosion, the impact of the PAGA on arbitration, and what to expect with PAGA rulings in 2024.
Trend #6 – PAGA Filings Reached An All-Time High
- The Explosion Of PAGA Notices
According to data maintained by the California Department of Industrial Relations, the number of PAGA notices filed with the LWDA has increased exponentially over the past two decades. The number grew from 11 notices in 2006, to 1,606 in 2013, and then experienced three sizable jumps – to 4,530 in 2014, to 5,732 in 2018, and to 7,780 in 2023, each coinciding with a significant shift in the legal landscape, as discussed below. From 2013 to 2014, employers saw the largest single year increase, from 1,605 notices in 2013 to 4,532 notices in 2014, an increase of 182%.
The most significant drop in the past two decades occurred in 2022, when notices fell from 6,502 in 2021 to 5,817 in 2022, before their resurgence in 2023.
The following chart illustrates this trend.
These numbers closely tie to the shifting landscape of workplace arbitration, as each of the major shifts coincides with the timing of a significant expansion or pull back in the law governing the enforcement of arbitration agreements.
- The PAGA As A Work-Around To Arbitration
The proliferation of mandatory arbitration programs started as early as 1991 when the U.S. Supreme Court issued Gilmer v. Interstate/Johnson Lane Corp., 500 U.S. 20 (1991). The movement did not gain steam, however, until 2011 when the U.S. Supreme Court issued its ruling in AT&T Mobility LLC v. Concepcion, 563 U.S. 333 (2011), and held that the Federal Arbitration Act (FAA) preempts state rules that stand “as an obstacle to the accomplishment of the FAA’s objectives.”
In the wake of AT&T Mobility, arbitration programs gained a boost in their popularity. Such programs provided companies a mechanism to contract around class and collective actions. Through a form agreement, offered as a condition of an employment relationship or transaction, for instance, a company could require its employees and customers to resolve any disputes on an individual basis through private, binding arbitration.
The growing popularity of such programs led the plaintiffs’ class action bar to identify work-arounds. The California Supreme Court cemented the PAGA as the frontrunner for employment-related claims with its decision in Iskanian v. CLS Transportation Los Angeles, 59 Cal.4th 348 (Cal. 2014). In Iskanian, the California Supreme Court seemingly immunized the PAGA from arbitration programs when it held that representative action waivers in arbitration agreements are “contrary to public policy and unenforceable as a matter of state law.” Id. at 384.
In rendering its decision, the California Supreme Court distinguished AT&T, reasoning that, whereas the FAA aims to ensure an efficient forum for the resolution of private disputes, a PAGA action “is a dispute between an employer and the state Labor and Workforce Development Agency.” Id.
Iskanian cleared the PAGA as a mechanism by which to maintain a representative action unhindered by arbitration agreements or commitments to arbitrate on an individual basis. The decision undoubtedly fueled the filing of PAGA notices in 2014, which catapulted from 1,606 in 2013 to 4,530 in 2014.
The PAGA workaround experienced another boost in October 2018, when the U.S. Supreme Court bolstered the enforceability of class and collective action waivers in arbitration agreements with its decision in Epic Systems Corp. v. Lewis, et al., 138 S.Ct. 1612 (2018), clearing the path to widespread adoption of arbitration programs. In the wake of Epic Systems, PAGA notices reached a new level, jumping from 4,984 in 2017, to 6,431 in 2019, reflecting PAGA’s expanding popularity as a work-around.
The PAGA-workaround movement suffered its first significant set-back in 2022 with the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Viking River Cruises, Inc. v. Moriana, et al., 142 S.Ct. 1906 (2022). In Viking River, the U.S. Supreme Court held that, to the extent Iskanian precludes division of PAGA actions into individual and non-individual claims, and thereby “prohibit[s] parties from contracting around this joinder device,” the FAA preempts such rule. Id. Thus, it concluded in the case before it that the lower court should have compelled arbitration of the plaintiff’s individual PAGA claims.
The U.S. Supreme Court then addressed the remaining question – what the lower court should have done with Moriana’s remaining non-individual or representative claims. The Supreme Court opined that the PAGA provides no mechanism to enable a court to adjudicate non-individual claims once an individual claim has been committed to a separate proceeding. As a result, the U.S. Supreme Court opined that Moriana lacked statutory standing to continue to maintain her non-individual claims in court, and the lower court should have dismissed the PAGA representative claims. Id.
Following Viking River, the number of PAGA notices suffered the largest single-year drop in two decades, dropping from 6,502 in 2021, to 5,817 in 2022.
- The PAGA’s Resurgence
Although the PAGA workaround suffered its first significant set-back in 2022 with the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Viking River, the set-back was short lived as, in 2023, the California Supreme Court minimized the impact of the Viking River decision.
In Adolph v. Uber Technologies, Inc., 14 Cal. 5th 1104 (Cal. 2023), the California Supreme Court took up the issue of whether, under California law, a PAGA plaintiff whose individual claims are compelled to arbitration retains standing to bring representative claims. The California Supreme Court disagreed with the U.S. Supreme Court’s interpretation of California law and held that, once a PAGA plaintiff’s individual claims are compelled to arbitration, the plaintiff retains standing to maintain non-individual PAGA claims in court so long as he is an “aggrieved employee.” Id. at 1105.
Adolph, an Uber delivery driver, asserted that Uber misclassified him as an independent contractor. Adolph amended his complaint to allege PAGA claims, and Uber moved to compel arbitration. The trial court denied Uber’s motion to compel arbitration, and the California Court of Appeal affirmed, citing the California Supreme Court’s ruling in Iskanian v. CLS Transportation Los Angeles, 59 Cal.4th 348 (2014). Uber filed a petition for review and, while it was pending, the U.S. Supreme Court issued its decision in Viking River.
In a unanimous decision, the California Supreme Court disagreed with the U.S. Supreme Court’s interpretation of the PAGA. The California Supreme Court held that, so long as an employee alleges that he has been aggrieved by a violation of the Labor Code, he maintains standing under the PAGA. As a result, after a court compels an individual PAGA claims to arbitration, the plaintiff retains standing to pursue his representative PAGA claims in court.
As to logistics, the California Supreme Court clarified several items. First, even though individual PAGA claims may be pending in arbitration and representative PAGA claims pending in court, the claims remain one action, and the court may stay the representative action pending completion of arbitration. Second, if the plaintiff loses in arbitration, at that point, the plaintiff loses standing to maintain representative PAGA claims. Third, if the plaintiff prevails in arbitration or settles his individual claims, he retains standing to return to court to pursue his representative PAGA claims on behalf of others.
By deciding that an individual who signs an arbitration agreement can return to court after arbitration to pursue representative proceedings under the PAGA, the California Supreme Court relegated arbitration agreements to a mere hurdle rather than a bar to PAGA representative actions. Given the technical requirements of California wage & hour law, coupled with the potentially crushing statutory penalties available to successful plaintiffs, we anticipate continued growth of PAGA lawsuits in 2024, with no pull back in site.
- What’s Next For The PAGA?
The California Supreme Court presently is considering two cases that significantly could impact the future popularity of PAGA lawsuits, including the ease with which plaintiffs can succeed in recovering on a representative basis.
On November 8, 2023, the California Supreme Court heard oral argument in Estrada, et al. v. Royalty Carpet Mills, Inc. The California Supreme Court is considering whether courts have the power to strike or limit PAGA claims based on unmanageability. In a prior decision, Wesson, et al. v. Staples the Office Superstore, LLC, 68 Cal. App. 5th 746 (2021), the California Court of Appeal held that trial courts have inherent authority to strike or limit unmanageable PAGA claims. A few months later, the Court of Appeal in Estrada, et al. v. Royalty Carpet Mills, Inc., 76 Cal. App. 5th 685 (2022), disagreed and concluded that, while a court may limit the presentation of evidence to ensure a manageable trial, a court does not have authority to strike or limit PAGA claims before trial. The California Supreme Court must issue a decision on this issue by February 2024. The California Supreme Court might hold that trial courts possess inherent authority to safeguard an employer’s due process rights, which necessarily encompasses the right to gauge the manageability of and to narrow PAGA claims. Either way, Estrada has the potential to significantly impact the prosecution and defense of PAGA actions.
In Turrieta, et al. v. Lyft, Inc., the California Supreme Court will weigh whether a PAGA plaintiff has a right to intervene, object to, or move to vacate a judgment approving a PAGA settlement in a related action. In that case, between May to July 2018, Olson, Seifu, and Turrieta, all Lyft drivers, filed separate PAGA actions alleging improper classification as independent contractors. Turrieta reached a $15 million settlement with Lyft, which included a $5 million payment to her counsel. As part of the settlement, Turrieta amended her complaint to allege all PAGA claims that could have been brought against Lyft. When Olson and Seifu got wind of the settlement, they moved to intervene and to object. The trial court denied the intervention requests, approved the settlement, and then denied motions by Olson and Seifu to vacate the judgment in the Turrieta PAGA action. The Court of Appeal affirmed, holding that, as non-parties, Olson and Seifu lacked standing to move to vacate the judgment. The Court of Appeal explained that the real party in interest in a PAGA action is the State, and, thus, neither Olson nor Seifu had a direct interest in the case.
Finally, in November 2024, California voters will pass on a proposed measure to repeal the PAGA and to replace it with a new law known as The Fair Pay and Employer Accountability Act. Under the proposed law, employees could not sue for civil penalties in court on behalf of the state and instead would have to file a complaint directly with the Labor Commissioner who would be a party to any lawsuit filed; all civil penalties would go to affected employees; the State would receive increased funding; and civil penalties would be doubled for “willful” violations. The measure is intended to eliminate the windfall profiteering that the plaintiffs’ bar has enjoyed from the PAGA. Although preliminary polling suggests voters support the measure, the plaintiffs’ bar surely will mount vociferous opposition.