By Alex W. Karasik, Gerald L. Maatman, Jr. and Jennifer A. Riley
Duane Morris Takeaways: The EEOC’s fiscal year (“FY 2024”) spans from October 1, 2023 to September 30, 2024. Through the midway point of FY 2024, EEOC enforcement litigation filings have been noticeably down. In the first six months of FY 2023, there were 29 new lawsuits filed by the Commission, while only 14 lawsuits were filed through the midway point of FY 2024.
Traditionally, the second half of the EEOC’s fiscal year – and particularly in the final months of August and September – are when the majority of filings occur. Even so, an analysis of the types of lawsuits filed, and the locations where they are filed, is informative for employers in terms of what to expect during the fiscal year-end lawsuit filing rush in September.
Cases Filed By EEOC District Offices
In addition to tracking the total number of filings, we closely monitor which of the EEOC’s 15 district offices are most active in terms of filing new cases over the course of the fiscal year. Some districts tend to be more aggressive than others, and some focus on different case filing priorities. The following chart shows the number of lawsuit filings by EEOC district office.
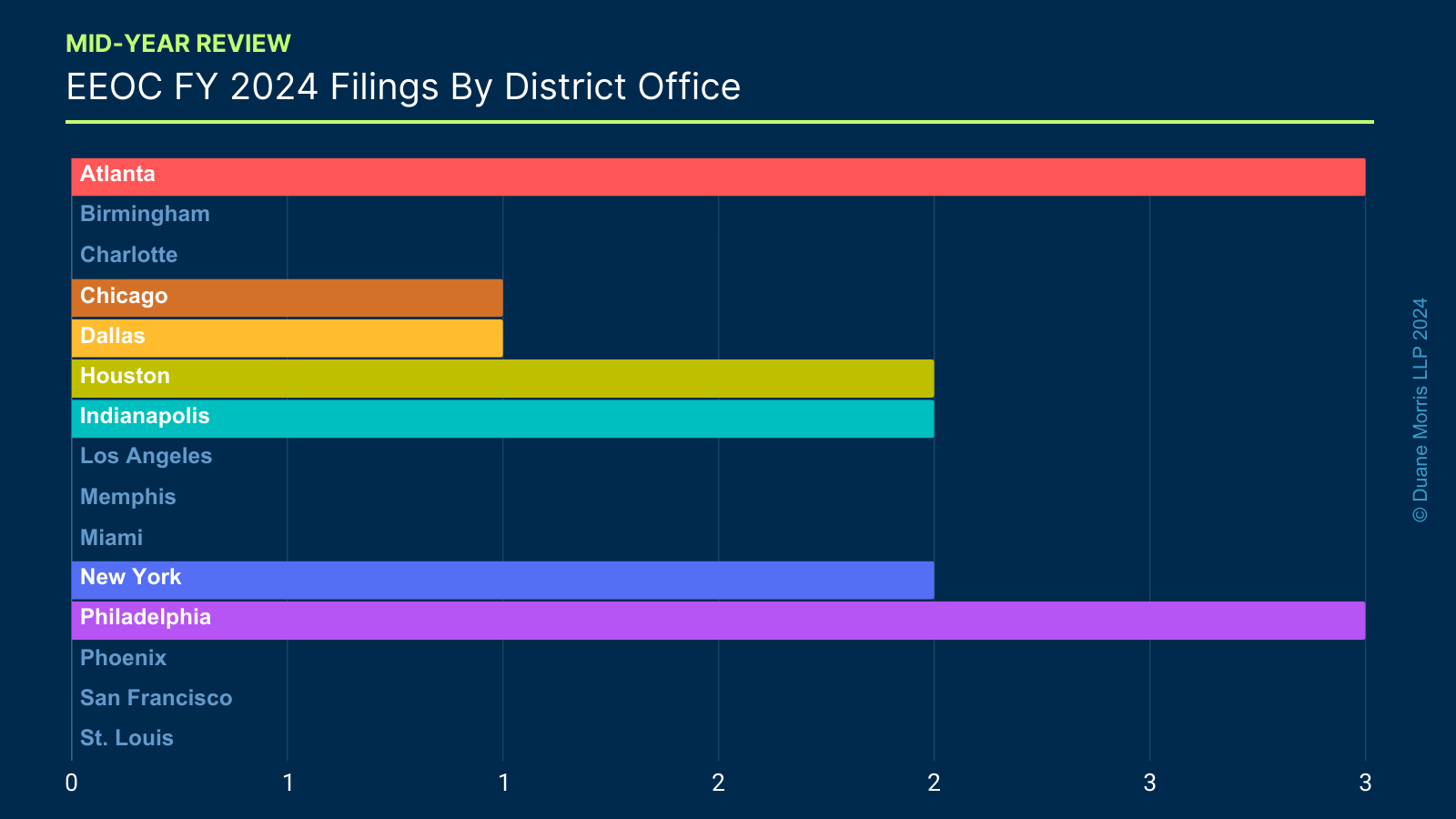
The most noticeable trend of the first six months of FY 2024 is that the Atlanta and Philadelphia District Offices already filed three lawsuits each. Houston, Indianapolis, and New York each have two lawsuit filings, and Dallas and Chicago have one each. That means that many of the district offices have yet to file a lawsuit at all in FY 2024. But for employers in the Atlanta and Philadelphia metropolitan areas, these early tea leaves suggest that a higher likelihood of pending charges may turn into federal lawsuits by the end of Summer to next Fall.
Analysis Of The Types Of Lawsuits Filed In First Half Of FY 2024
We also analyzed the types of lawsuits the EEOC filed throughout the first six months, in terms of the statutes and theories of discrimination alleged, in order to determine how the EEOC is shifting its strategic priorities. The chart below shows the EEOC filings by allegation type.
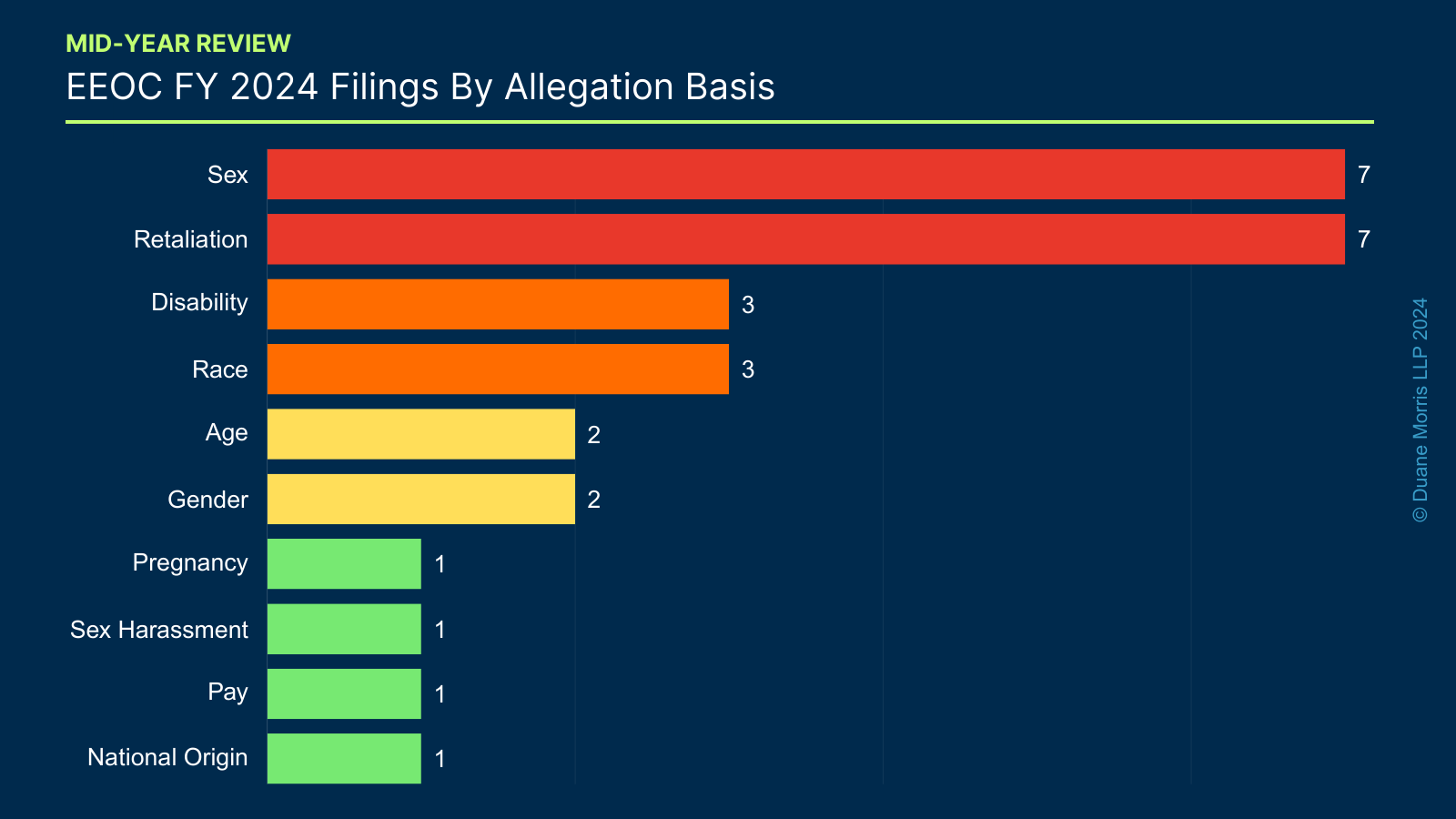
The percentage of each type of filing has remained fairly consistent over the past several years. However, in FY 2024, nearly every filing has contained Title VII claims, with 12 of the 14, or 87% alleging these violations. This is a major increase over past years — in FY 2023, Title VII claims in 59% of all filings, 69% in FY 2022, and 62%. ADA cases were alleged in three lawsuits filed, for 21% of the cases, a decrease from the EEOC’s FY 2023 filings of 31%, 18% in FY 2022, and 36% in FY 2021. There was also an ADEA claim in one of the lawsuits and Pregnancy Discrimination Act claim in another.
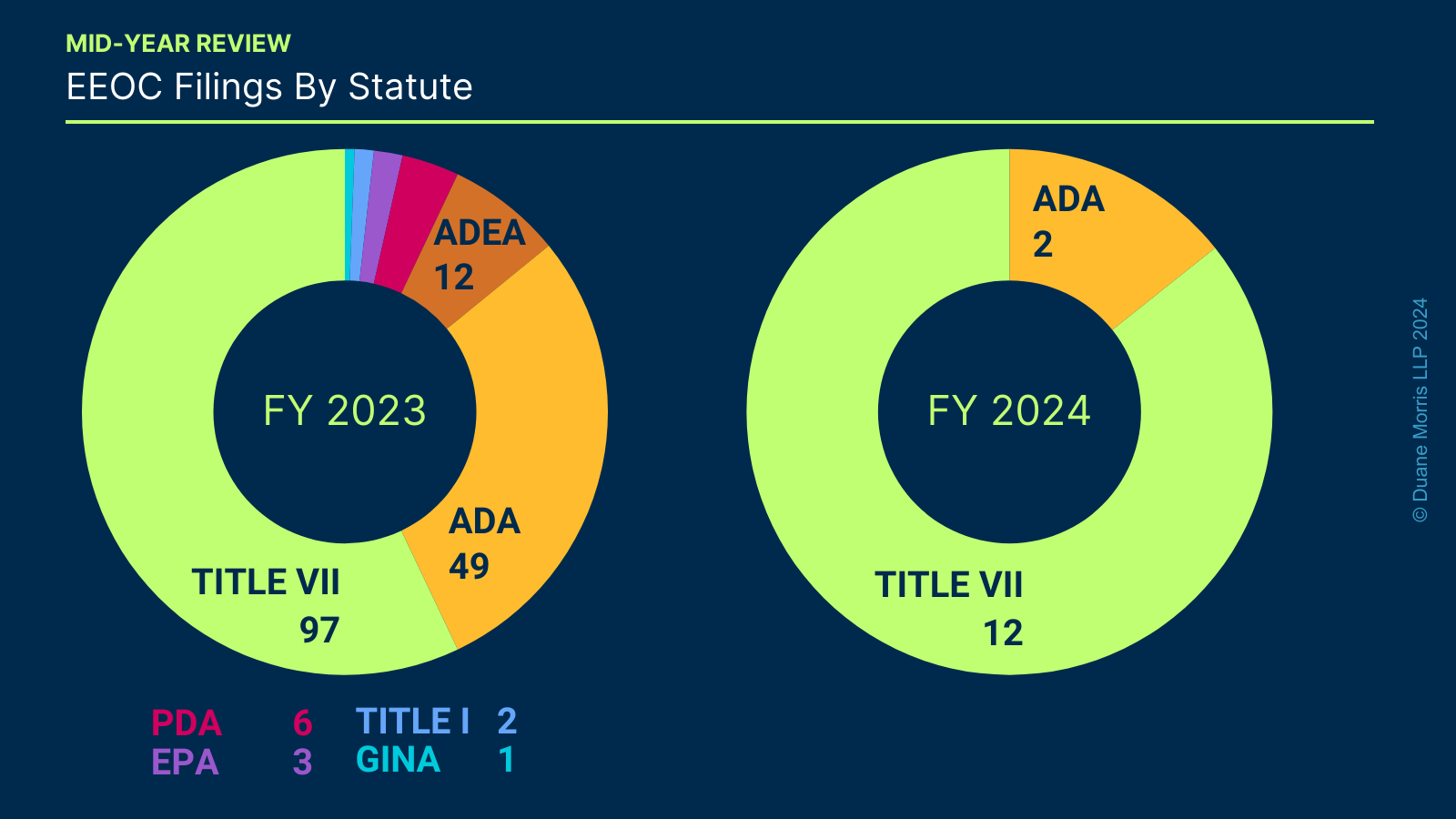
The graph set out below shows the number of lawsuits filed according to the statute under which they were filed (Title VII, Americans With Disabilities Act, Pregnancy Discrimination Act, Equal Pay Act, and Age Discrimination in Employment Act) and, for Title VII cases, the theory of discrimination alleged.
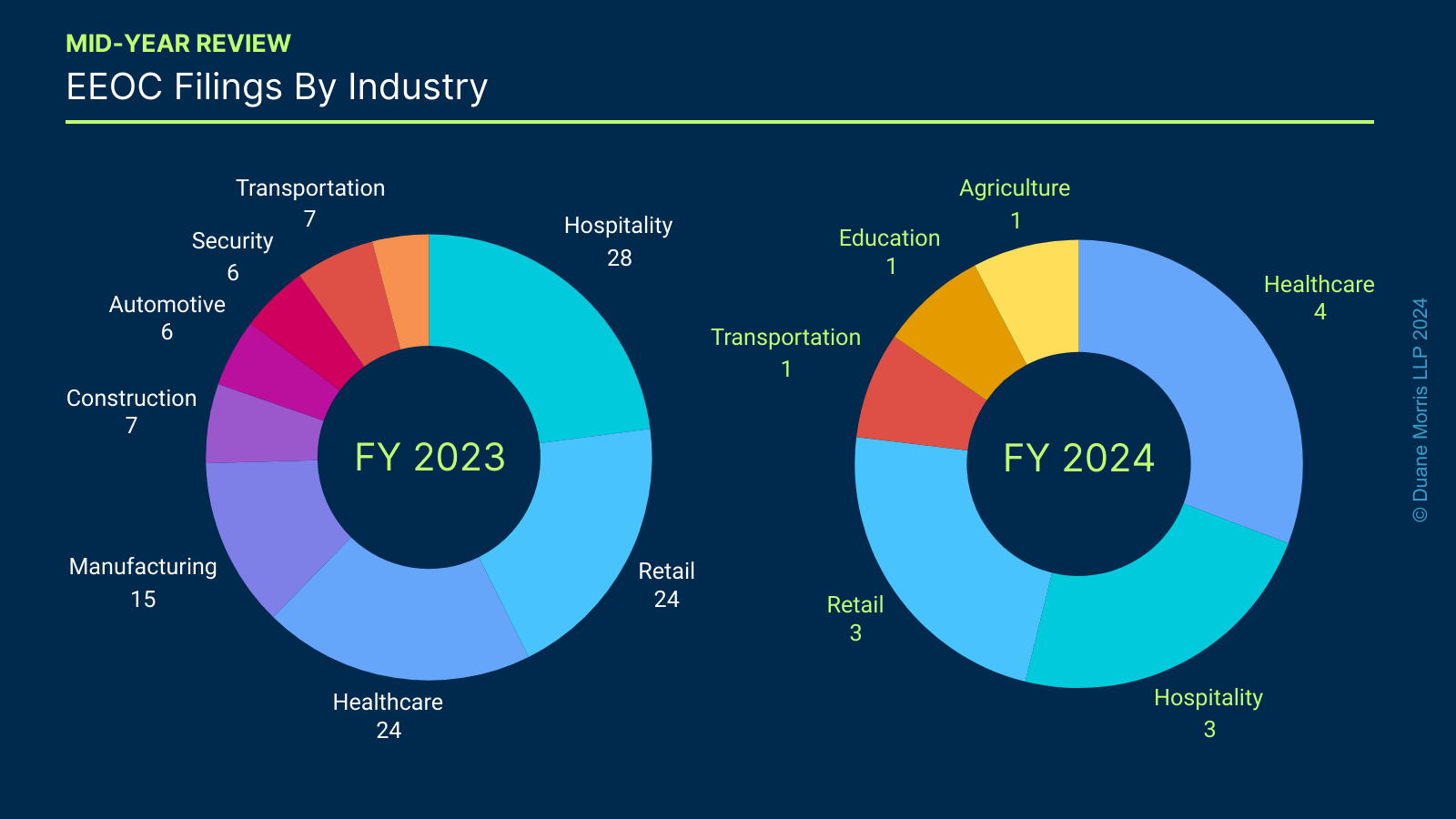
The industries impacted by EEOC-initiated litigation have also remained consistent in FY 2024. The chart below details that hospitality, healthcare, and retail employers have maintained their lead as corporate defendants in the last 18 months of EEOC-initiated litigation.
Notable 2024 Lawsuit Filings
Gender Identity Discrimination
In EEOC v. Sis-Bro, Inc., Case No. 24-CV-968 (S.D. Ill. Mar. 28, 2024), the EEOC brought suit alleging that the farm violated federal law when it allowed an employee to be harassed because of her sex and gender identity after she began transitioning genders. The EEOC contended that the employee was subjected to frequent, derogatory comments about the employee’s gender identity; the co-owner refused to call the targeted employee by her name and referred to her by her former name; repeatedly told her she was “a guy”; and criticized her use of employer-provided health insurance and leave for gender affirming care, in violation of Title VII of the Civil Rights Act.
Disability Discrimination
In EEOC v. Atlantic Property Management, Case No. 24-CV-10370 (D. Mass. Oct. 4, 2023), the EEOC filed an action on behalf of a new hire who the company allegedly rescinded a job offer following the employee’s cancer diagnosis. The EEOC alleged that the individual was offered employment as an executive administrative assistant to the president and vice president of the two companies. Shortly after the offer of employment, the employee was diagnosed with breast cancer. Her doctor confirmed she was able to perform all aspects of her position, but she would need to receive treatment weekly resulting in a need for some limited time off from work. When she provided her doctor’s note to the companies, the president decided to withdraw her job offer without any discussion with the employee, which the EEOC alleged violated the ADA.
Race / National Origin Discrimination
In EEOC v. Bob’s Tire Company, Case No. 24-CV-10077 (D. Mass. Jan. 10, 2024), the EEOC filed an action alleging that the company violated Title VII of the Civil Rights Act by subjecting employees to egregious and constant harassment, including the owner telling Hispanic employees to “go back to [their] country”; calling Guatemalan employees “f—ing Guatemalans”; donning a U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement hat to intimidate Hispanic employees; and calling employees homophobic slurs. Additionally, the EEOC contended that employees were also harassed by a co-worker because of their sex, race, and national origin, and at least one employee complained to the owner, who retaliated against this complaining employee by mocking him for being in a romantic and/or sexual relationship with the harassing co-worker.
These filings illustrate that the EEOC will likely continue to prioritize sex, disability, and race discrimination claims in the second half of FY 2024.
March 2024 Release Of Enforcement Statistics
On March 12, 2024, the EEOC published its fiscal year 2023 Annual Performance Report (FY 2023 APR), highlighting the Commission’s recovery of $665 million in monetary relief for over 22,000 workers, a near 30% increase for workers over Fiscal Year 2022. This annual publication from the EEOC is noteworthy for employers in terms of recognizing the EEOC’s reach, understanding financial exposure for workplace discrimination claims, and identifying areas where the EEOC may focus its litigation efforts in the coming year. It is a must read for corporate counsel, HR professional, and business leaders.
As we blogged about here, the Commission reported having one of the most litigious years in recent memory in FY 2023, with 142 new lawsuits filed, marking a 50% increase from FY 2022. Among these new lawsuits, 86 were filed on behalf of individuals, 32 were non-systemic suits involving multiple victims, and 25 were systemic suits addressing discriminatory policies or affecting multiple victims. The EEOC also touted that it obtained $22.6 million for 968 individuals in litigation, while resolving 98 lawsuits and achieving favorable results in 91% of all federal district court resolutions.
These numbers show the EEOC is still aggressively litigating discrimination claims, and despite the slow start in FY 2024, we anticipate the EEOC will turn up the jets in the second half of the fiscal year.
Strategic Priorities
The Commission also reported significant progress in its “priority areas” for 2023, which included combatting systemic discrimination, preventing workplace harassment, advancing racial justice, remedying retaliation, advancing pay equity, promoting diversity, equity, inclusion and accessibility (“DEIA”) in the workplace, and, significantly, embracing the use of technology, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other automated systems in employment decisions.
In 2023, the EEOC resolved over 370 systemic investigations on the merits, resulting in over $29 million in monetary benefits for victims of discrimination. The Commission also reported that its litigation program achieved a 100% success rate in its systemic case resolutions, obtaining over $11 million for 806 systemic discrimination victims, as well as substantial equitable relief. Further, the Commission made outreach and education programs a priority in 2023, and specifically sought to reach vulnerable workers and underserved communities, including immigrant and farmworker communities, hosting over 680 events for these groups and partnering with over 1,120 organizations, reaching over 107,000 attendees.
These statistics confirm the Commission’s prowess, dictating that employers should take heed in the coming months as the EEOC seeks to match these gaudy figures.
Other Notable Developments
Beyond touting its monetary successes, and litigation accomplishments, the FY 2023 APR also highlights the newly enacted Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (“PWFA”), which provides workers with limitations related to pregnancy, childbirth, or related medical conditions the ability to obtain reasonable accommodations, absent undue hardship to the employer.
The Commission began accepting PWFA charges on June 27, 2023 (the law’s effective date) and has conducted broad public outreach relating to employers’ compliance obligations under the new law.
Takeaways For Employers
By all accounts, FY 2023 was a record-breaking year for the EEOC. As demonstrated in the report, the Commission has pursued an increasingly aggressive and ambitious litigation strategy to achieve its regulatory goals. The data confirms that the EEOC had a great deal of success in obtaining financially significant monetary awards.
Although the early numbers are lagging as compared with last year, we anticipate that the EEOC will continue to aggressively pursue its strategic priority areas in FY 2024. There is no reason to believe that the annual “September surge” is not coming, in what could be another precedent-setting year. We will continue to monitor EEOC litigation activity on a daily basis, and look forward to providing our blog readers with up-to-date analysis on the latest developments.
Finally, we are thrilled to announce that will be providing a webinar on May 13, 2024, to further analyze the above data. Employers will gain insight on what they should be doing to ready themselves for the remainder of FY 2024. Save the date and stay tuned!