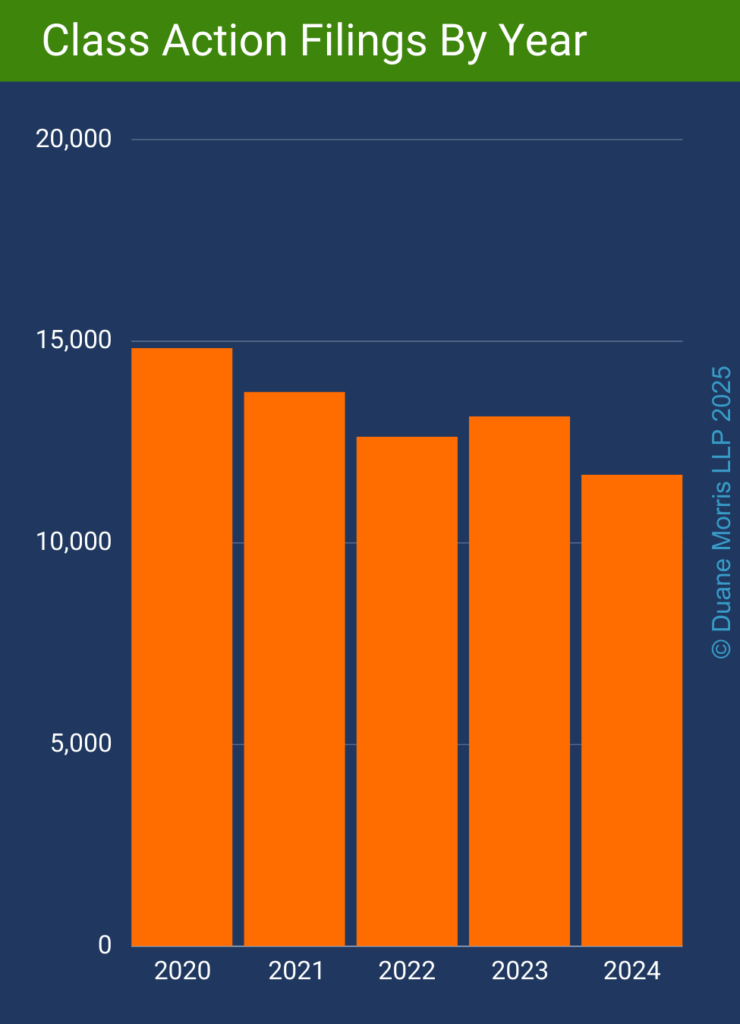
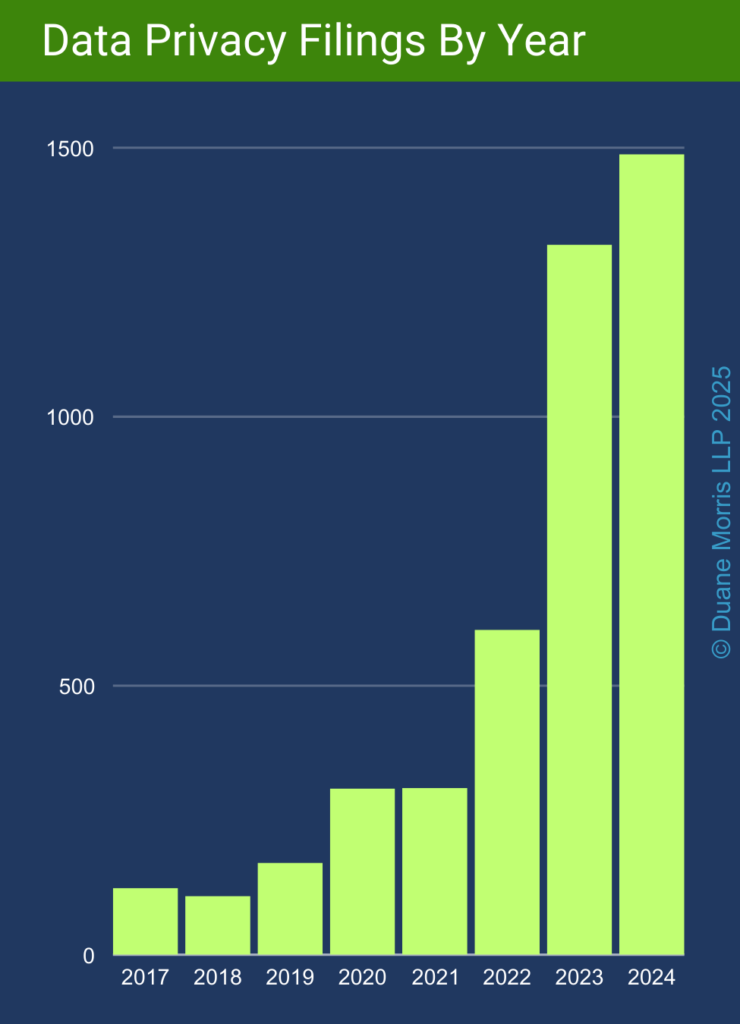
By Gerald L. Maatman, Jr.
Duane Morris Takeaway: The U.S. Supreme Court’s 2023 decision in Students for Fair Admissions, Inc. (SFFA), et al. v. President & Fellows of Harvard College, 600 U.S. 181 (2023), stimulated a flood of claims targeting diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs over the past year. Headlines were replete with cases of employees and applicants accusing employers of prioritizing diversity over merit and improperly using protected characteristics to guide decision-making, setting the stage for more class action activity in this area.
In SFFA, the U.S. Supreme Court held that two colleges and universities that considered race as a factor in their admissions processes violated the Equal Protection Clause of the U.S. Constitution and Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Although the decision did not arise in the employment context, or involve Title VII, the Supreme Court’s decision striking down the use of racial preferences has caused an increase in class action lawsuits and other claims challenging (i) employers’ DEI programs, (ii) alleged misrepresentations about their DEI programs, and (iii) other environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives.
Watch the video below with partner Jerry Maatman to hear more about this trend:
Since the U.S. Supreme Court struck down affirmative action in college admissions, plaintiffs have filed a flood of challenges to corporate DEI programs, claiming that they constitute impermissible “reverse discrimination” under Title VII. Headlines this past year were replete with cases of employees and applicants accusing employers of prioritizing diversity over merit and improperly using protected characteristics to guide decision-making. In 2024, courts issued a number of rulings in these cases, with mixed results, typically dependent on the nature of the allegations at issue in the lawsuit. In general, companies found more success in overcoming these challenges where their challenged DEI programs were focused more on colorblind issues like eliminating implicit bias and fostering inclusivity, and less success when focused on achieving numerical diversity quotas and other actions perceived as demonizing white males. See, e.g., De Piero v. Pennsylvania State University, 711 F. Supp. 3d 410 (E.D. Pa. 2024) (granting in part and denying in part employee’s reverse discrimination claims); Young v. Colorado Department Of Corrections, 94 F.4th 1242 (10th Cir. 2024) (affirming dismissal of employee’s reverse discrimination claim); Herrera v. New York City Department Of Education, 2024 WL 245960 (S.D.N.Y. Jan. 23, 2024) (denying defendants’ motion for summary judgment on employees’ reverse discrimination claims); Duvall v. Novant Health, Inc., 95 F.4th 778 (4th Cir. 2024) (affirming verdict for employee alleging reverse discrimination).
In October 2024, a rare class action trial in California in Palmer, et al. v. Cognizant Technology Solutions Corp., Case No. 17-CV-6848 (C.D. Cal.), led a jury to find a technology firm liable for engaging in a pattern or practice of discrimination against Caucasian and non-Indian employees in its termination and deployment decisions. The plaintiffs alleged the technology firm favored Indian and South Asian employees for whom it sponsored H-1B visas. The jury concluded, based on statistical evidence presented at trial, that the technology firm engaged in a pattern or practice of discrimination by terminating non-Indian and non-South Asian employees at a much higher rate than its other employees (8.4 times more likely).
In 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court granted certiorari in a reverse discrimination lawsuit, with a decision likely to be rendered in 2025 that will have implications for reverse discrimination lawsuits of all types, including class actions, moving forward. At issue in Ames, et al. v. Ohio Department of Youth Services, No. 23-1039 (U.S. cert granted Oct. 4, 2024), is whether, in addition to pleading the other elements of an employment discrimination claim under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, a majority-group plaintiff must show “background circumstances to support the suspicion that the defendant is that unusual employer who discriminates against the majority.” The Supreme Court is poised to resolve a federal circuit split over this issue, potentially opening the courthouse to more such claims.
Although many companies’ DEI programs remain strong post-SFFA with an increased emphasis on inclusivity and ensuring compliance with anti-discrimination laws, other companies have begun stepping down their DEI commitments for a variety of reasons, including the fear of a backlash of reverse discrimination claims. Companies that step down their DEI commitments, however, should take care to ensure that their public-facing statements regarding those commitments remain true.
More generally, all companies should take care to ensure that they are not overstating or misrepresenting their policies and practices regarding DEI and other social issues. Such overstatements are known as “diversity washing” or “woke washing,” and are increasingly forming the basis of class action lawsuits alleging securities fraud or other misrepresentations.
In 2024, federal courts denied motions to dismiss in two diversity-washing class actions, for example, finding that plaintiffs plausibly stated claims for intentional misrepresentations. See Craig, et al. v. Target Corp., 2024 WL 4979234 (M.D. Fla. Dec. 4, 2024) (denying motion to dismiss securities fraud class action alleging misrepresentations regarding the risk of customer boycotts from ESG, DEI, and LGBT initiatives); SEB Inv. Management AB v. Wells Fargo & Co., 2024 WL 3579322 (N.D. Cal. July 29, 2024) (denying motion to dismiss securities fraud class action alleging false or misleading statements regarding corporation’s requirement that 50% of job interview candidates be diverse).
Companies’ statements regarding their DEI commitments have been voluntary to date. As a result, diversity-washing claims have applied only to statements companies have elected to make. However, many more public company statements about diversity may be forthcoming and subject to complaints filed by the plaintiffs’ class action bar, pending a challenge in the Fifth Circuit to SEC-approved Nasdaq rules requiring any of the over 3,000 companies listed with the Nasdaq with at least five board members to either have two board members from an underrepresented group or explain why not. The Fifth Circuit previously upheld these Nasdaq board diversity rules over a challenge under the First and Fourteenth Amendments to the U.S. Constitution, the Securities Exchange Act, and the Administrative Procedure Act. See Alliance For Fair Board Recruitment v. SEC, 85 F.4th 226 (5th Cir. 2023). In 2024, the Fifth Circuit vacated that opinion and reheard the case en banc, on May 14, 2024. If the Nasdaq board diversity rule is upheld, it will take full effect in December 2026.
The label “ESG” has become mainstream in the past few years. ESG refers broadly to “environmental, social, and governance,” which many companies have embraced as part of their business plans and corporate missions. Whereas diversity-washing class actions focus on the “S” in ESG, class actions also recently have proliferated relative to overstatements regarding environmental issues, thus highlighting the “E” in “ESG.”
These “greenwashing” class actions continued to proliferate in 2024. See Dorris, et al. v. Danone Waters of America, 2024 WL 4792048 (S.D.N.Y. Nov. 14, 2024) (dismissing greenwashing class action); Fanucchi v. Enviva Inc., 2024 WL 3302564 (D. Md. July 3, 2024) (dismissing greenwashing class action); Boyd, et al. v. Target Corp., 2024 WL 4287669 (D. Minn. Sept. 25, 2024) (denying motion to dismiss greenwashing class action).
As companies continue to add statements regarding their environmental impact or social responsibility to enhance their marketing efforts, communicate their company values, and/or attempt to appeal to consumers and shareholders attuned to ESG considerations, we expect to see ESG class actions continue their growth trajectory.